EXAMINING TOURIST NEEDS THROUGH MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS AND THE ROLE OF HOTEL ANIMATION
Julia Lazoura, , University of West Attica
Laloumis Athanasios, , University of West Attica
Geronikolas Harris, , University of West Attica
Mitsopoulos Dimitrios, University of West Attica
Abstract
It is considered vital to refer to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs when dealing with tourists needs. On the other hand we should take into consideration the role of hotel animation people towards these needs. As each one of us step into roles to the society we live in. These roles help define ourselves but also develop our personalities. The way we act during holidays and how the hotel animation staff would interfere to the roles tourists adopt is a subject of this article. It is vital to acknowledge the necessary qualities that animateurs have according to their expertise and how these qualities impact on the tourists needs.
Key words: tourism, needs, hotel animation, Maslow
INTRODUCTION
Human needs during tourism consumption are different than those from daily life. As holidays means putting an end of the one way of life and making a start to another. Under this thinking Tourism can be examined as a procedure that gives human the opportunity to create a unique cocktail in making their own way of life which seems greater or better at that moment.
Of course not all customers have the same needs, in the same form or in the same tension. Others have their relax holidays others their adventure ones to have fun, to isolate etc. Although hotels mostly cover their needs they are not able to fulfil everything like peace in the country or access to it (Sarris, 1985).
THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
There are various theories according to human needs and their role to human behaviour. One of the most important is Maslow’s theory and the one presented in this article. Maslow refused to agree that human behaviour is led through independent impulses. Some of the existing schools of thought of his time (behaviourism or psychoanalysis) focused more on problematic behaviours and their explanation. He tried to define cohesion and coherence to the trends of human behaviour and became interested in learning what makes people happy and how they achieve that. Maslow was a humanist so he believed that humans seek self actualization as a desire coming from their human nature. However in order to achieve that basic needs should be met. The five levels of Maslow’s theory are widely known as the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
He supported that:
- Humans are constantly led from their needs as they become aware of them
- Needs shouldn’t be examined individually.
- The obstruction of a need in whichever level tends to hold this level as a priority.
- The needs are classified in priority sequence, as:
1. Survival needs for food, air, shelter, sex
2. Needs for safety and stability
3. Social needs of companionship, friendship and affection.
4. Social status needs and respect.
5. Self actualization through success and evolution
Survival needs are the primary needs of human. But when these are fulfilled then human focuses on next level of the safety needs. The rule goes that when a need is fulfilled is no longer at the longing point. When the survival and safety needs are covered humans tend to move on to cover the rest of their needs.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs gives the necessary basis to approach and understand the tourism needs that hotel animation is due to cover. These needs have to be covered according to the hierarchy. Firstly and for the whole duration of the customer’s stay the primary as well as safety needs should be fulfilled not only in quantity but also in quality. Special interest should be spent to cover social and self actualization needs accordingly. These needs are focused on the human try to maximize the evolution (Laloumis, 1999)
The fulfilment of the needs is accomplished as a whole and pro rata meaning that after the vital cover of human life need, the satisfaction of the other categories comes to light while the one incomplete need seek fulfilment.
The fulfilment of a need procedure leads to cover other needs as well. So the meal at an excursion may cover the need of food but also makes the contact between the customer and Greek gastronomy offering knowledge, satisfying the need for making acquaintances, having fun or company.
The human needs are important when they are not satisfied. When satisfied are due to exist. Motivation of human behaviour usually stays deeper, secret and the demonstration of a need or a desire cannot be interpreted so easily (Harper & Row, 1971).
Humans of a social group are attached through an evaluation pattern that is specific for the group. Each individual maintain his individuality. Under this evaluation pattern of the group some of the needs are easily satisfied while others are restrained. The pattern limits the various options of personality and presses to uniformity. The evaluation process makes spontaneity impossible. The spontaneous answer to fulfil the unconscious needs is blocked mainly through the evaluation process. From the individual reactions to the team’s pattern a person’s personality and his values can be identified (Freud, 1974).
In an ideal society, the needs of its members would be satisfied directly and immediately without any restrains or conflicts between values’ systems of it. Something closely similar is the target of hotel animation but under no circumstances can this be met entirely as, till today, no human ever satisfied all his needs. Animation though, offers the opportunity to approach the quality of life which an ideal society promises (Sarris, 1999).
Spending his free time creatively trying to cover the uncovered needs each person longs for distance from daily labour. Maslow’s hierarchy is not fulfilled in exact sequence on a daily basis but vice versa. The self actualization needs come first towards the primary ones. 85% of his primary needs are covered to every one of us, 70% of safety ones, 50% of his social needs, 40% of respect needs but only 10% of self actualization. The remaining gap to each step towards the free time activities shown to the table below results in that free time activities act as antimotives to the ones of life (table 1).
The amount of needs that have a connection with tourism are called tourism needs. Tourism needs can be divided to two main categories. The ones before the trip and the ones during the trip. Before the trip needs that motivate the person to do the trip are the ones that affect his choices. These needs can be called tourism motives.
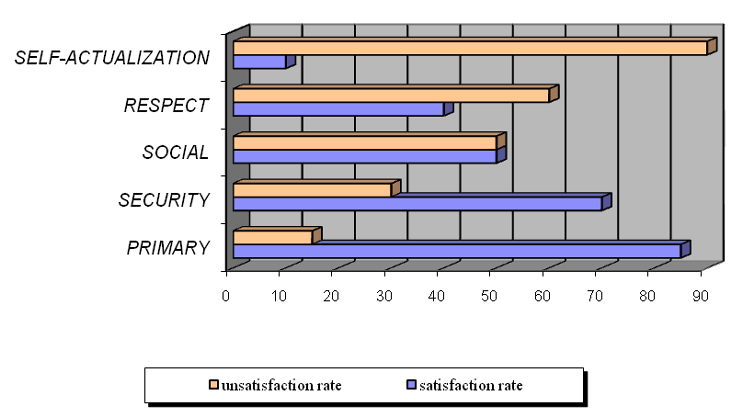
Table1: satisfaction of needs towards free time activities
Tourism motives to destination are transformed to actual needs. For example a need that leads the person to tourism is the connection with nature that he seeks. To tourism destination, each person becomes active in order to cover that need having excursions, walks etc.(Laloumis, 2014).
The natural social needs among other needs that each person has in his habitat don’t affect tourism. They continue to be tourists’ needs. But the satisfaction means of these needs differ, forming a special net of needs.
Tourist needs before taking the trip are a part of a person’s ambitions. During the trip become goals that are reached according to the variety and the form of tourist offer. Human needs at the same time take a tourist form. Generally tourists want to take a taste of locality through local food, local dances and fairs and get an interactive approach to local life. In hotel clubs this kind of locality is obvious and determined.
CONLCUSION
Hotels in general thrive to offer a clean room, good food and as much as possible better service in quality or quantity. Meeting the needs referred above as tourists’ needs is something that not just hotels but hotel animation specifically is sure to achieve. Even if we start from scratch and that is the materialistic needs to cover the primary needs or safety and security ones or better yet the self actualization needs, hotel clubs are sure to cover them more than successfully. Living close to nature, relax at the pool bar and socializing, hotel animation and its trained people are there to fulfill any desire not only physically but mentally or psychologically. The network of means and the necessary mechanism is being built under the prism of human needs therefore the tourists ones, and how to successfully cover them.
REFERENCES
Allport Gordon “Pattern and Growth in Personality” Holt Rinehart and Winston, N.Y. 1961, p.454
Beck Ulrich, «Κοινωνία της Διακινδύνευσης», Αθήνα, 2015, p.148-163
Dimaki, A., 2009. The Great Importance of Corporate Identity in Hospitality Management, Tourism Issues, Vol. 10, September 2009, 54-67.
Freud S., “Ο Πολιτισμός είναι Πηγή Δυστυχίας” Αθήνα, 1974 p.19
Grotte, Judit, New Trends in the Hospitality Industry, 2015 : 11 pp. 174-189. , 16 p. (2015) https://www.jotr.eu/pdf_files/V11.pdf
Harper & Row N.Y. “Motivation and Personality” 1970, p.172
Laloumis A., Bouda V., 13,14,15/6/2010, 2ο international Conference of Hospitality Management. Subject: “Interaction in Tourism between Employees and Tourists. Is there a Vavel?”, pp. 514 - 527
Murphy Gardner “Social Motivation” στο “Handbook of Social Psychology”, Allison – Wesley, Lindzay 1954, V. 2, p.629
Marinakos, K., Laloumis, D. (2012) The satisfaction of tourists from the provided hotel services: The Peloponnese as a case study. Journal of Tourism Research, Vol.4, pp.201- (ISSN:2241 – 7931)
McDougall «Introduction in Social Psychology» 1908 (p. 172-181)
J. Petrof «Διοίκηση marketing», Πειραιάς 1977
Tischler Henry ‘Introduction to Sociology’ Αθήνα, 2019 p.192-209
Λαλούμης Δ., «Διοίκηση Ανθρώπινου Δυναμικού Τουριστικών Επιχειρήσεων» σελ. 177-188
Λαλούμης Δ., «Ξενοδοχειακή Ψυχαγωγία και Άθληση» εκδ. Σταμούλης 1999 σελ.48-61
Νεοκλής Σαρρής «Ψυχοκοινωνιολογία του κινηματογράφου» περιοδικό «Ψυχολογία» Τ.2 σελ.274-281
Παπαγεωργίου Γ.Κ. «Ψυχολογία» Ψυχοτεχνική, Ηράκλειο Κρήτης, 1985
